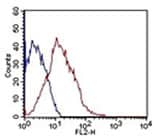
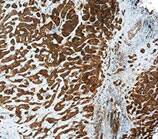
Novus antibodies have been cited over 1,300 times in research relating to breast cancer and its associated diseases. We are proud to offer high quality antibodies that help researchers probe the underlying causes and possible treatments for breast cancer patients. Cited Novus Antibodies for Breast Cancer Research
|